📝 Introduction to NestJS with CRUD Example
🌟 What is NestJS?
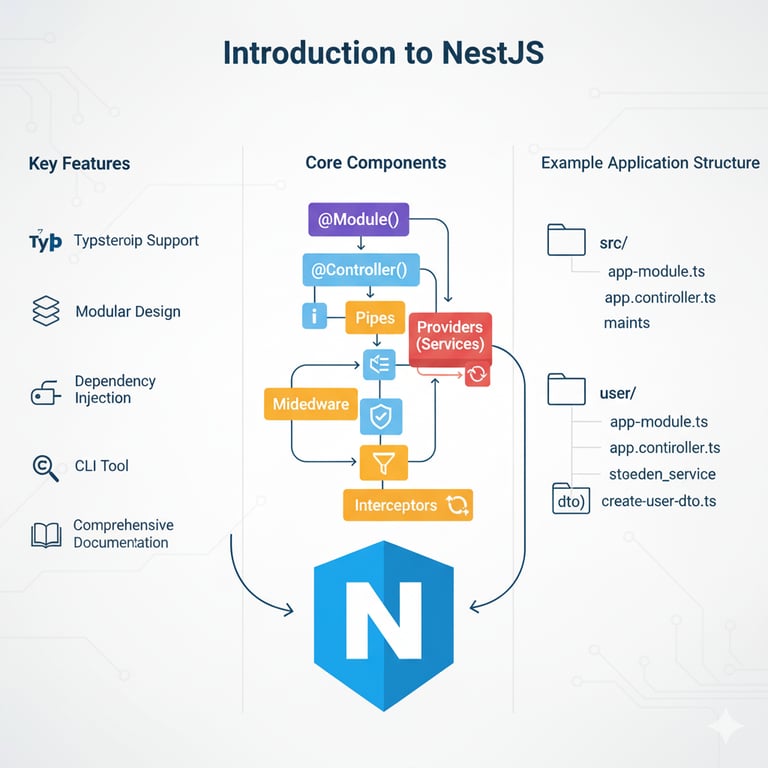
NestJS is a progressive Node.js framework built with TypeScript. It helps developers build scalable and maintainable backend applications by providing structure and features like:
Modules → Group related features (like
PropertyModule).Controllers → Handle incoming requests and send responses.
Services → Contain business logic (optional in small demos).
Decorators → Special keywords like
@Controller,@Get,@Postto define routes.
Think of NestJS as a structured version of ExpressJS. If ExpressJS is minimal and flexible, NestJS is organized and opinionated, making it great for larger projects.
⚙️ Setup
Install NestJS CLI globally:
npm i -g @nestjs/cliCreate a new project:
nest new property-apiMove into the project folder:
cd property-apiRun the server in development mode:
npm run start:dev
📂 Folder Structure
When you generate a new module and controller for property, NestJS organizes code like this:
src/
│── main.ts
│── app.module.ts
│
└── property/
│── property.module.ts
│── property.controller.ts
📝 Complete CRUD Example
src/main.ts
import { NestFactory } from '@nestjs/core';
import { AppModule } from './app.module';
async function bootstrap() {
const app = await NestFactory.create(AppModule);
await app.listen(3000);
console.log('🚀 Server running on http://localhost:3000');
}
bootstrap();
src/app.module.ts
import { Module } from '@nestjs/common';
import { PropertyModule } from './property/property.module';
@Module({
imports: [PropertyModule],
})
export class AppModule {}
src/property/property.module.ts
import { Module } from '@nestjs/common';
import { PropertyController } from './property.controller';
@Module({
controllers: [PropertyController],
})
export class PropertyModule {}
src/property/property.controller.ts
import { Controller, Get, Post, Put, Delete, Param, Body } from '@nestjs/common';
let properties = [
{ id: 1, name: 'Property One', type: 'Condo' },
{ id: 2, name: 'Property Two', type: 'House' }
];
@Controller('property')
export class PropertyController {
// GET all
@Get()
findAll() {
return properties;
}
// GET one
@Get(':id')
findOne(@Param('id') id: string) {
return properties.find(p => p.id == id) || { message: 'Not found' };
}
// POST create
@Post()
create(@Body() body: any) {
const newProperty = { id: properties.length + 1, ...body };
properties.push(newProperty);
return newProperty;
}
// PUT update
@Put(':id')
update(@Param('id') id: string, @Body() body: any) {
const property = properties.find(p => p.id == id);
if (!property) return { message: 'Not found' };
Object.assign(property, body);
return property;
}
// DELETE
@Delete(':id')
remove(@Param('id') id: string) {
properties = properties.filter(p => p.id != id);
return { message: `Property ${id} deleted` };
}
}
🚀 How to Test
GET →
http://localhost:3000/property→ Returns all propertiesGET →
http://localhost:3000/property/1→ Returns one propertyPOST →
http://localhost:3000/property→ Adds new propertyPUT →
http://localhost:3000/property/1→ Updates propertyDELETE →
http://localhost:3000/property/1→ Deletes property
✅ With this simple CRUD example, you’ve learned:
How NestJS apps are structured
How to use
@Controller,@Get,@Post,@Put,@DeleteHow to handle routes, parameters, and body data
👉 Next step: Compare this with ExpressJS CRUD example to see the difference in style and complexity.
Would you like me to add the ExpressJS CRUD example immediately after this NestJS section (so readers can directly compare)?
Nest.js Vs Express.js |Comparison
Compare NestJS vs ExpressJS with simple CRUD examples. Learn which Node.js framework is best for quick apps or scalable backend development
Read Full StoryWhy Do Front-End Frameworks Exist?
Modern frameworks like React, Vue, and Angular exist because building complex, interactive apps with just plain JavaScript quickly becomes unmanageable. Let’s look at how web development evolved and why frameworks are the solution.
Read Full StoryIntroduction to Node.js (Full Interview Guide)
Explore Node.js with our concise infographic detailing its core functionalities. Learn how this JavaScript runtime powers fast, scalable backend development, real-time apps, and robust APIs. Perfect for developers and businesses looking to understand Node.js benefits.
Read Full Story🛣️ Node.js Roadmap
Explore a comprehensive Node.js roadmap. Discover key stages for learning and mastering Node.js development, from foundational concepts to advanced topics.
Read Full Story