Why Do Front-End Frameworks Exist?
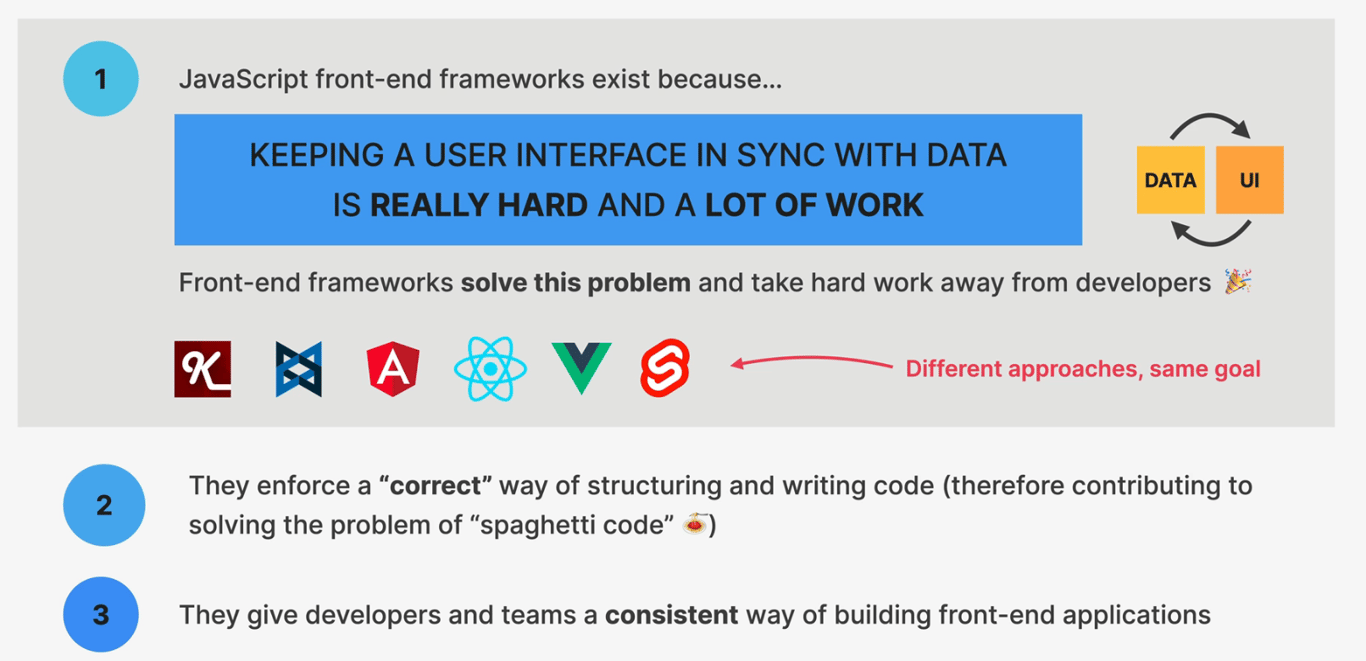
 Modern frameworks like React, Vue, and Angular exist because building complex, interactive apps with just plain JavaScript quickly becomes unmanageable.
Modern frameworks like React, Vue, and Angular exist because building complex, interactive apps with just plain JavaScript quickly becomes unmanageable.
Let’s look at how web development evolved and why frameworks are the solution.
1️⃣ The Evolution of Web Development
Era | What Happened | Typical Tools |
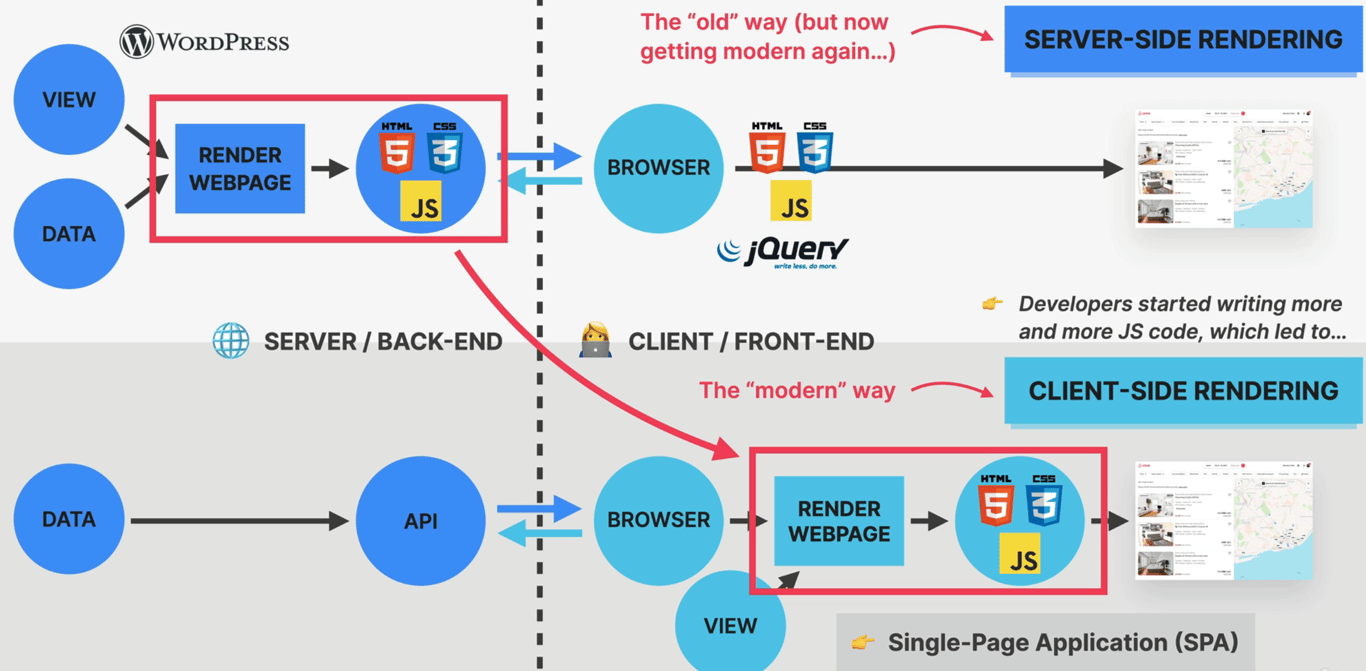
Pre-2010 | All pages were server-rendered: the backend built HTML, CSS, and small JavaScript, which was sent to the browser. | WordPress, PHP, JSP |
Early 2010s | JavaScript grew → more interactivity. jQuery became king for cross-browser DOM tricks. | jQuery, small scripts |
Mid-2010s | Single-Page Applications (SPAs): The client renders the UI, and data comes via APIs. Apps start feeling native. | React, Angular, Vue, Backbone |
2020+ | Hybrid approaches: SSR + CSR combined for the best of both worlds. | Next.js, Remix, Nuxt |
2️⃣ SPAs in a Nutshell
One HTML page, navigation handled on the client side.
Data fetched via APIs (JSON).
UI updates instantly without full reloads.
State (filters, forms, maps, etc.) lives in JavaScript and must stay in sync with UI.
Example: Airbnb – apartments list, map, filters, search box all depend on and update each other.
3️⃣ Why Vanilla JS (and jQuery) Break Down for Large Apps
Problem | What It Looks Like | Why It Breaks |
Massive DOM manipulation |
| Spaghetti code → hard to maintain. |
State stored in the DOM | Data embedded in | Multiple parts of the app are changing the DOM → bugs & inconsistencies. |
No structure | Mix of logic, UI, and state updates. | Teams write code differently → messy, unscalable. |
👉 Result: Hard to reason about, bug-prone, not scalable.
💀 Example: jQuery Counter (Problematic)
HTML
<p id="counter">Clicked 0 times</p>
<button id="btn">Increment</button>
<script src="https://code.jquery.com/jquery-3.6.0.min.js"></script>
<script>
let count = 0;
$("#btn").click(function () {
count++;
$("#counter").text("Clicked " + count + " times");
// Now imagine if you had another element
// also showing count — you must update it manually too.
// Forgetting one causes the UI to go out of sync!
});
</script>
👉 With jQuery, every time the state changes, you must manually update every place in the DOM.
As apps grow (like Airbnb’s filters + maps + lists), this quickly becomes fragile and unmanageable.
4️⃣ How Frameworks Solve These Problems
Feature | Benefit |
Declarative UI | You describe what UI should look like → framework updates the DOM for you. |
Centralized State Management | All app data managed in one place → UI stays in sync automatically. |
Components & Reuse | Self-contained building blocks → modular, testable, reusable code. |
Performance Optimizations | Virtual DOM, batching, lazy loading → faster apps. |
Enforced Structure | Consistent patterns (components, props, state) → less spaghetti code. |
Ecosystem & Tooling | Hot reload, routing, SSR/SSG support, testing, dev tools. |
Team Collaboration | Shared conventions → easier onboarding, consistent codebase. |
5️⃣ Code Example: Vanilla JS vs React
Vanilla JavaScript (manual DOM updates)
HTML
<p id="counter">Clicked 0 times</p>
<button id="btn">Increment</button>
<script>
let count = 0;
const p = document.getElementById("counter");
const btn = document.getElementById("btn");
btn.addEventListener("click", () => {
count++;
p.textContent = `Clicked ${count} times`;
});
</script>
React (declarative)
JavaScript
function App() {
const [count, setCount] = React.useState(0);
return (
<div>
<p>Clicked {count} times</p>
<button onClick={() => setCount(c => c + 1)}>Increment</button>
</div>
);
}
➡️ With React, you just declare what the UI should look like given count. React handles the DOM updates.
6️⃣ Side-by-Side Comparison
Aspect | Past (SSR) | Vanilla JS / jQuery SPAs | Frameworks |
Rendering | Server builds a full page. | Client renders via manual DOM updates. | Auto-rendering via Virtual DOM/reactivity. |
JavaScript Role | Small enhancements only. | Entire UI logic done manually. | UI auto-syncs with state changes. |
State Management | Minimal (server-driven). | Stored in DOM → messy. | Centralized, predictable state. |
Complexity | Simple/static pages. | Spaghetti code in large apps. | Modular components, clean structure. |
User Experience | Full page reloads. | SPA feel, but fragile updates. | Native-like smooth UX. |
Performance | Server-bound. | Slow, manual DOM updates. | Optimized, scalable. |
Team Work | Small, not critical. | Inconsistent coding styles. | Conventions → consistency. |
Scalability | Fine for blogs. | Breaks at Airbnb-scale. | Built for large apps. |
Trends | SSR only. | Pure client SPAs. | Hybrid SSR + CSR. |
✅ The Bottom Line
Without frameworks: managing state + DOM manually (even with jQuery) leads to spaghetti code, bugs, and poor scalability.
With frameworks: The data and UI stay in sync automatically, code is modular and consistent, apps are performant and maintainable.
👉 Frameworks like React, Vue, and Angular exist to abstract away complexity, enforce structure, and let developers focus on building great user experiences instead of wrestling with DOM and state.
Class-Based vs Functional Components in React - Key Differences for Interviews
Learn the key differences between class-based and functional components in React, including lifecycle methods, hooks, state management, and interview tips. This is one of the most common React interview questions, as it directly relates to React lifecycle methods. React components are the building blocks of a React application, and understanding their differences helps you write efficient, maintainable code.
Read Full StoryNest.js Vs Express.js |Comparison
Compare NestJS vs ExpressJS with simple CRUD examples. Learn which Node.js framework is best for quick apps or scalable backend development
Read Full StoryWhat is JavaScript? A Complete Beginner's Guide
Learn what JavaScript is, how it works, and how to add it to your web pages with inline, external, async, and defer script loading strategies.
Read Full Story📝 Introduction to NestJS with CRUD Example
Beginner-friendly NestJS tutorial with CRUD example. Learn setup, folder structure, and simple GET, POST, PUT, DELETE API routes in NestJS.
Read Full Story